How to Delete a Directory in Linux Safely (30 Proven Methods)

If you've ever needed to clean up your Linux system, then you've probably wondered how to delete a directory in Linux without messing things up. This guide covers every method, command, and best practice to delete Linux directories like a pro, while avoiding critical errors.
Understanding How to Delete a Directory in Linux
Before running any command, it’s vital to understand what happens when you delete a directory in Linux. A directory is just a folder containing files or subfolders. When you remove it, everything inside it also vanishes unless handled carefully.
Basic Concepts of Linux File Hierarchy
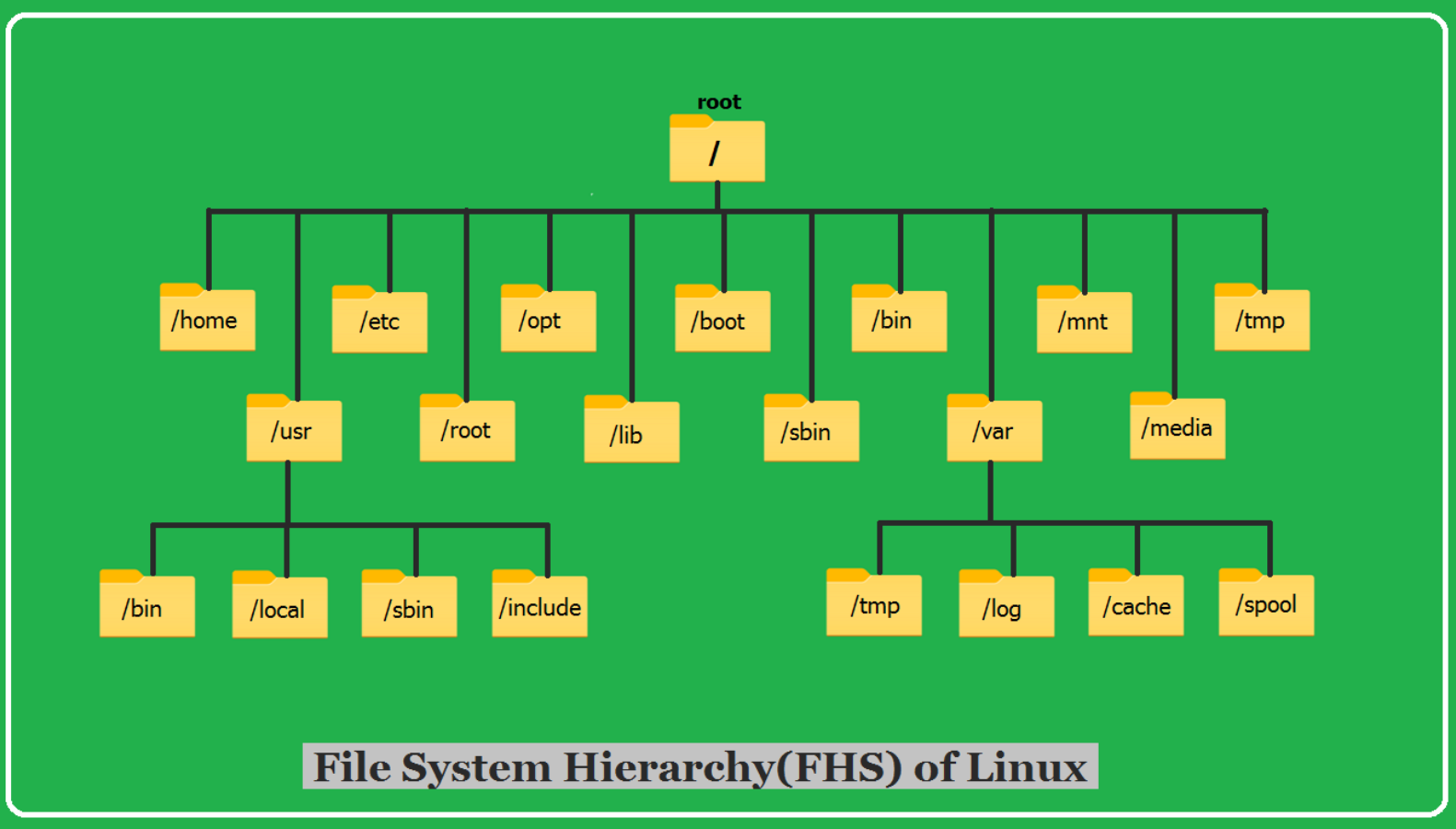
- Root (
/): The top of the directory tree. - User Directory (
/home/username): Where personal files reside. - System Directories (
/etc,/bin,/var): Critical system folders.
Avoid deleting anything under / or system directories unless you know exactly what you're doing.
Essential Terminal Commands for Linux Directory Operations
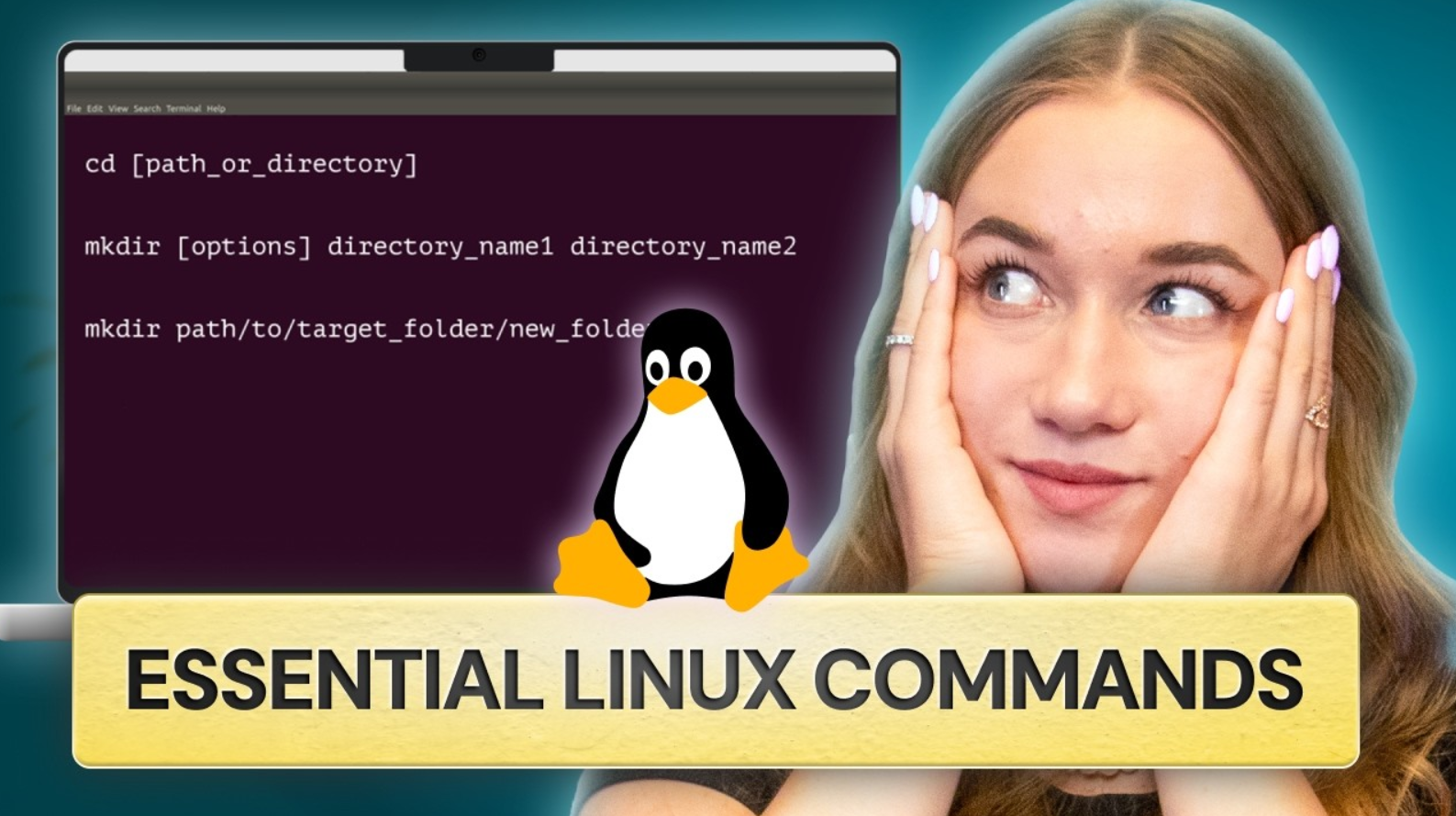
You must be comfortable using the terminal. Below are key commands:
cd: Change directoryls: List directory contentspwd: Show present working directorysudo: Run command with administrative privileges
When Should You Delete a Directory in Linux?
You may need to delete directories in Linux to:
- Free up disk space
- Remove obsolete projects or logs
- Automate cleanup via scripts
- Manage user home directories
Method 1: How to Delete an Empty Directory Using rmdir
Syntax:
rmdir directory_name
Use Case:
- Best for directories without any files
- Doesn’t delete non-empty folders
Example:
rmdir /home/user/testfolder
If the directory contains anything, it will show:rmdir: failed to remove 'folder': Directory not empty
Method 2: How to Delete a Directory in Linux Using rm -r
Syntax:
rm -r directory_name
Why Use It?
- Works on directories with files
- Recursive deletion of contents
Example:
rm -r /home/user/tempfiles
Caution:
- It prompts before deletion
- Always verify the path before pressing Enter
Method 3: Using rm -rf for Forceful Directory Deletion
Syntax:
rm -rf directory_name
Flags Explained:
-r: Recursive-f: Force (no confirmation)
Example:
rm -rf /home/user/cache
Warning:
Never run rm -rf / — it wipes the entire OS.
Method 4: Delete Directories Using Wildcards
Examples:
- Delete all folders starting with “temp”:
rm -r temp*
- Delete all folders ending in “logs”:
rm -r *logs
Use wildcards carefully to avoid mass deletion of unintended directories.
Method 5: Delete Multiple Directories in One Command
Syntax:
rm -r folder1 folder2 folder3
Use this when you want to remove several folders at once without writing multiple commands.
How to Confirm That a Directory Has Been Deleted
Use:
ls
or check programmatically:
[ -d folder ] && echo "Exists" || echo "Deleted"
Graphical Interface (GUI) Method to Delete a Directory
For users on Ubuntu, Fedora, or any GNOME based system:
- Open Files
- Right-click the folder
- Select Move to Trash
- Empty Trash manually
This is perfect for users not comfortable with terminal commands.
How to Recover Accidentally Deleted Directories in Linux
- Use Timeshift or rsync backups
- Use trash-cli if you used the safe delete method
- In critical cases, tools like extundelete may help (filesystem-specific)
Permission Issues When Deleting Linux Directories
If denied:
sudo rm -r folder_name
Use ls -ld folder_name to check permissions before attempting deletion.
Common Deletion Errors and Solutions
- Directory not empty: Use
rm -r - Permission denied: Add
sudo - File not found: Check for typos
Using Shell Scripts to Automate Directory Deletion
Sample Bash Script:
#!/bin/bash
rm -rf /home/user/temp/*
How to Run It:
chmod +x delete.sh
./delete.sh
Useful for server cleanups or scheduled maintenance.
Find and Delete Specific Directories
Command Example:
find /path -type d -name "backup*" -exec rm -r {} +
Powerful for filtered deletion based on name, date, or content.
How to Securely Delete a Directory in Linux
Prevent recovery of deleted data using:
srm -r folder_name
You can also use shred or overwrite the data multiple times before deletion.
Delete Hidden Directories (Dotfiles)
Command:
rm -rf .folder_name
Make sure you run ls -a to see hidden folders before deleting.
Handling Symbolic Links
To delete a symlink:
rm link_name
This does not delete the actual directory it points to.
What to Do with Read-only File Systems
Remount it as writable:
mount -o remount,rw /mountpoint
Then perform your deletion.
Unmount Before Deleting Mounted Directories
Steps:
- Unmount the drive:
umount /mnt/data
- Then delete the mount point:
rm -rf /mnt/data
Safe Deletion Using trash-cli
Install:
sudo apt install trash-cli
Use:
trash-put folder_name
Restore:
trash-restore
Perfect for adding a safety net to terminal deletions.
Log Deleted Directories
Add this line to your .bashrc or .zshrc:
alias rm='rm -i; echo "$(date): $@" >> ~/delete.log'
This keeps a log of what you’ve deleted.
Preventing Accidental Deletions
- Always use
-iflag - Alias
rmtorm -i - Double-check the folder name
- Never use
sudo rm -rfcasually
Schedule Directory Deletion with cron
Add this to crontab:
0 3 * * * rm -rf /home/user/temp/*
This deletes the folder every day at 3:00 AM.
Use Aliases for Safer Deletion Commands
In .bashrc:
alias rm='rm -i'
Prevents accidental file deletion by prompting for confirmation.
Never Delete System Directories
Never delete:
/etc/boot/usr/bin
Doing so will destroy your Linux installation.
Measure Disk Space Before and After Deletion
du -sh folder_name
This shows how much space a directory takes up.
Legal and Ethical Guidelines for Deletion
Always:
- Get permission if working on shared systems
- Use backups
- Comply with data retention laws
Best Practices for How to Delete a Directory in Linux
- Understand your file system
- Use
rm -iortrash-put - Log deletions
- Schedule cleanups
- Train users on safe deletions
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I recover a deleted directory in Linux?
Only if you've used tools like trash-cli or backup utilities.
What does rm -rf / do?
It tries to delete every file on the system, rendering it unusable.
How do I delete directories owned by root?
Use sudo rm -r directory_name.
How to delete only empty directories?
Use:
find /path -type d -empty -delete
Can I undo a rm -rf command?
Not directly. Only backups can help.
What is the safest way to delete a directory in Linux?
Use trash-cli or rm -ri for safety and confirmations.
Conclusion: Mastering How to Delete a Directory in Linux
You’ve now mastered the skill of how to delete a directory in Linux—safely, efficiently, and in a way that protects your system from accidental damage. Use the correct command for your context, always verify paths, and remember: a backup is your best friend.